Section 3.1.1
Section 3.1.1 - General Database Access
Connection to (or working with) the ‘Microsoft SQL Server ORMGP Database’ can be accomplished through a variety of software packages, potentially using a number of different protocols. Examples include:
- Microsoft SQL Management Studio (version 2019, 2016, …)
- Microsoft Access and Excel (Office versions 2016, 2010, …)
- EarthFX Viewlog (version 4; some capability in version 3))
- EarthFX SiteFX (version 5)
- Other - any software that supports an ODBC (or similar) connection (e.g. some GIS software, Microsoft Visual Studio, etc …; not described here)
Microsoft Access and Excel
Access and Excel gain access to the SQL database through a DSN (Database Source Name) file. The DSN file typically provides the data source name and directory, the server address, user ID and password, and other information. The DSN file can be created as a ‘User DSN’ or as a ‘File DSN’, the difference being that the latter will be stored as plain text in a separate accessible file while the former will store the connection information in the system registry. Either can be used (in general, the ‘User DSN’ is used by Access while the ‘File DSN’ is used by Excel). The DSN file has the following form and would have a ‘.dsn’ extension:
[ODBC]
DRIVER=SQL Server Native Client 11.0
UID=sqlmirror
DATABASE=OAK_20160831_MASTER
WSID=MDM6500
APP=Microsoft? Windows? Operating System
Trusted_Connection=Yes
SERVER=SQLSERVER2K16
To create the necessary DSN files the following procedure can be followed. Connection by these software packages is enabled through the ‘ODBC Data Source Administrator’ installed on most Windows operating system’s (executable name is ‘odbcad32’ or ‘odbcad32.exe’, generally found under the ‘C:\Windows\System32’ path). Note that, depending on the agency’s IT policies, a user’s permission to access and run this software may be restricted. Where access is available or has been enabled by IT staff, running this program will result in the following dialog box opening:
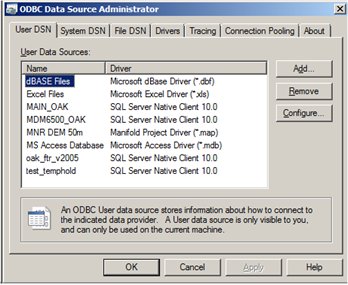 Figure 3.1.1.1 ODBC Data Source Administrator user
dialog box.
Figure 3.1.1.1 ODBC Data Source Administrator user
dialog box.
Under the ‘User DSN’ tab, select ‘Add - SQL Server Native Client … - Finish’. This brings up a new dialog box:
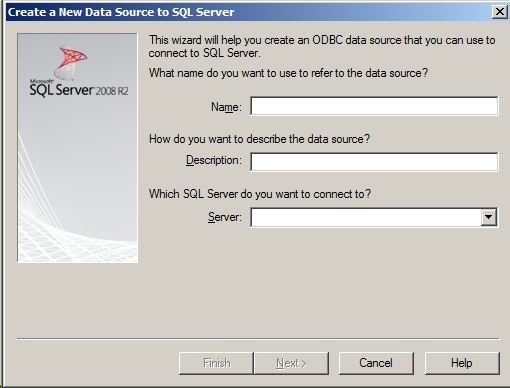 Figure 3.1.1.2 Create a New Data Source to
SQL Server dialog box
Figure 3.1.1.2 Create a New Data Source to
SQL Server dialog box
This box allows the user to specify the parameters for connection to the SQL Server running at the partner agency. Specify:
- a ‘Name’ (in the form OAK_20120615_PARTNER, where ‘Partner’ refers to your agency e.g. OAK_20160831_MASTER)
- a short description (e.g. ‘ORMGP master database, version 20160831’)
- the server (or instance) name on which the database is being hosted - this will be site dependent.
The following will need to be configured (on a subsequent windows dialog box, after ‘Next’ is selected; this information will be included as part of the DSN specification)
- Specify ‘Integrated Windows authentication’ or ‘SQL Server authentication’
- Change the ‘default database’ to OAK_20160831_MASTER
- Select ‘Use ANSI quoted identifiers’
- Select ‘Use ANSI nulls, …’
Select ‘Test Data Source’ (when available) as a check that the parameters have been specified correctly (a ‘TESTS COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY’ should be returned; otherwise there is a problem). At this point (once the final dialog box has been closed and the DSN has been successfully created) the ‘Name’ (specified previously) should be listed as an option under the ‘User DSN’ tab of the ‘ODBC Data Source Administrator’ (i.e. in the first box shown above).
In the same ‘ODBC Data Source Administrator’ box (as shown above) the file-based connection can also be created using the above procedure but under on the ‘File DSN’ tab instead of the ‘User DSN’ tab (the result won’t be shown in the window but, instead, be present as a file in a user-specified location).
Once the DSN files have been created, Access and Excel can be connected to the database. For using Microsoft Access to connect to the database, select (once an Access database has been opened) ‘File - Get External Data - Link Tables’ and ‘Files of type - ODBC Databases’. Here the user will be able to browse to a DSN file (under ‘File Data Source’) or select the user-specified ‘Name’ (e.g. OAK_20160831MASTER) under ‘Machine Data Source’. A ‘Link Tables’ dialog box will come-up from which the user can specify which tables (or views, which are treated as tables in Access) to link to. Note that the user should link the tables (rather than import; the latter should only be used when the user wants to create a snapshot/cut of the data which will then be totally separate from the main database). Also, only tables containing (as the first two characters) D*, R_* or V_* should be linked (the remainder are system tables which should not be linked to ensure no changes are made to them).
For using Microsoft Excel to connect to the database, select (once an Excel worksheet has been opened) ‘Data - Import External Data - Import Data’ then select ‘Files of Type - ODBC File DSNs (*.dsn)’. The user can then navigate to the location of their previously created ‘File DSN’. Alternatively, the user can select ‘New Source’ which will allow creation of a new connection akin to the above method described for Microsoft Access (note that this will be saved as an ODC (Office Database Connections with an ‘.odc’ extension) file.
EarthFX SiteFX and Viewlog
Both SiteFX and Viewlog use an ODBC file (containing the appropriate parameters and with an ‘.odbc’ extension) to link into a SQL Server database. They are generally of the following form (all the information should appear on a single line in the ODBC file):
ODBC;DRIVER={SQL Server};DATABASE=OAK_20160831_MASTER;SERVER=SQLSERVER2K16; Trusted_Connection=yes;
OR
ODBC;DRIVER={SQL Server};DATABASE=OAK_20160831_MASTER;SERVER=SQLSERVER2K16; UID=dbuser; pwd=12345678
The first example is using a ‘Trusted Connection’ to connect to the partner database - usually a ‘Windows Domain Account’ (a single username/password combination to login to any computer on the partner’s network). The second example uses a ‘SQL Server Account’ which only allows access to the server/database combination specified. In most cases, the first form (with the substitution of the appropriate database and server name) would be used.
Other Software
Note that additional software may use one of (or a combination of) the methods described above. In addition, individual software packages may have built-in methods by which to connect and access information from the SQL Server. Refer to the documentation for these packages.
